By Dr. Ara Deukmedjian, MD
Board-Certified Neurosurgeon, Deuk Spine Institute
Medically reviewed on February 10, 2026
Medical disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Individual results may vary. Always consult with your healthcare provider about your specific condition and treatment options.
Key Points
Before diving into the details, here’s what you need to know about L5-S1 disc herniation and its possible connection to abdominal pain:
✓ L5-S1 is the most stressed spinal segment – Located at the base of the spine where the lumbar region meets the sacrum, this segment bears the highest mechanical load.
✓ 95% of lumbar disc herniations occur at L4-L5 or L5-S1 – Making L5-S1 the most common site for disc-related problems.
✓ Sciatica is the hallmark symptom – Pain radiating down the leg, rather than abdominal pain, is the most typical presentation.
✓ Abdominal pain from L5-S1 is referred, not direct – The disc itself doesn’t directly cause digestive issues.
✓ Ventral (front-facing) disc herniations can compress sympathetic nerves – Though rare, this can cause pelvic or abdominal pain in documented cases.
✓ Referred pain mechanisms are complex – Such pain arises from neural convergence within the spinal cord, not from direct organ involvement.
✓ Secondary gastrointestinal symptoms are common – Postural changes, stress, and reduced mobility can indirectly affect digestion.
✓ Cauda equina syndrome is a medical emergency – Sudden bowel or bladder dysfunction requires immediate medical care.
✓ MRI plus clinical correlation is essential – Imaging alone cannot fully determine the source of pain.
✓ Minimally invasive treatment options exist – Procedures such as Deuk Laser Disc Repair address the root cause with a 99.6% success rate and no reported complications.
For millions of people, persistent discomfort in the lower back is more than just an annoyance. It’s often a sign of a deeper spinal problem. The L5-S1 herniation, located at the very base of the spine, is arguably the most common cause of severe, life-altering back and leg pain.
However, some patients experience symptoms that seem unrelated to the spine, such as digestive discomfort or sharp abdominal pain. So, is there a genuine connection between a herniated disc and stomach health?
This article offers a science-backed explanation of L5-S1 herniation, clarifies its hallmark symptoms such as debilitating sciatica, explores the debated link to referred abdominal pain, and highlights the most advanced treatment options available today.
The Anatomy of Back Pain: Understanding the L5-S1 Junction
To understand the problems that arise from a disc issue, it’s important to first recognize the crucial function of this specific area of the spine. The L5-S1 segment is the transition point between the lumbar spine (L5 vertebra) and the sacrum (S1 segment); is arguably the most stressed region in the entire back.
The Critical Role of the L5-S1 Disc
The L5-S1 disc, often referred to as the lumbosacral disc, is uniquely positioned to withstand massive biomechanical loads. It sits precisely where the spine transitions from the flexible lumbar column to the rigid pelvis. As the junction responsible for nearly all body weight transfer and most movements: such as lifting, bending, and twisting. The disc endures significant compressive and shear forces.
Research indicates that about 95% of lumbar disc herniations occur at the L4-L5 or L5-S1 levels.1 A 2024 study further found that combined herniation at both L4-L5 and L5-S1 was the most common pattern, observed in 28.8% of patients.2
Structurally, the disc consists of two key components: the tough, fibrous annulus fibrosus, and the soft, gel-like nucleus pulposus. This dual design enables the spine to absorb shock while maintaining flexibility and stability.

How a Herniation Occurs at L5-S1
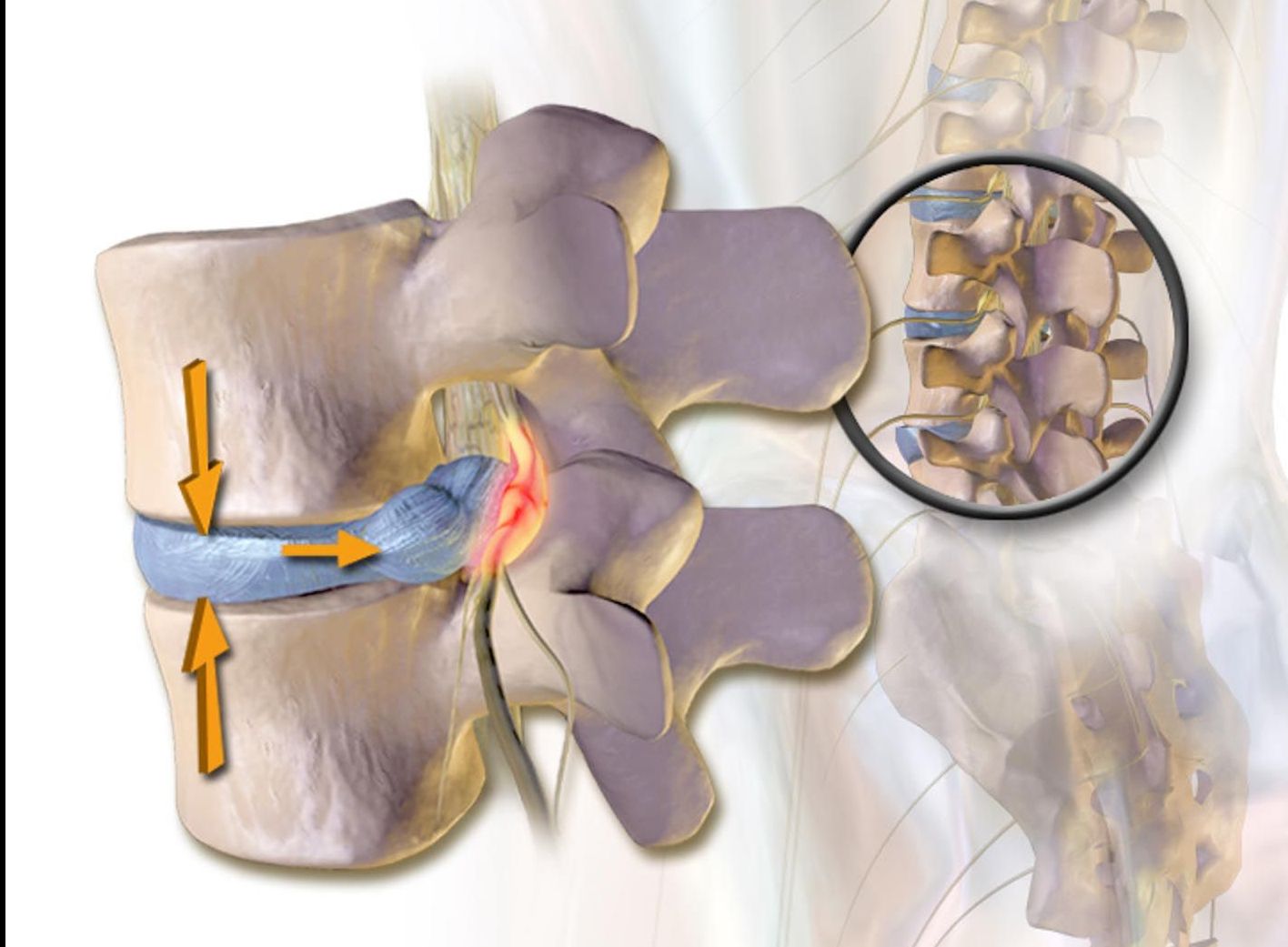
An L5-S1 herniation occurs when the annular fibers tear, allowing the soft nucleus pulposus to protrude outward. This tearing process is often the direct source of a specific form of back pain known as discogenic pain.
Discogenic pain presents as a deep, persistent ache localized to the lower back. It results from inflammatory chemicals released by the nucleus pulposus and from direct irritation of nerve endings within the torn annulus. Such tears may develop suddenly from trauma. Such as lifting a heavy object or gradually from chronic degeneration, repetitive strain, or poor posture.
Once the disc material herniates, it can compress or irritate nearby spinal nerves, producing the classic radicular symptoms that radiate down the leg.
Nerve Roots and the Lumbosacral Plexus
The L5-S1 level is critical because it is where the L5 and S1 nerve roots exit the spine. The L5 nerve root controls foot movement and provides sensation along the outer shin and the top of the foot. The S1 nerve root governs the calf muscles and transmits sensation along the back of the leg and the sole of the foot.
These nerve roots form the primary components of the lumbosacral plexus, a complex network that supplies motor and sensory function to the entire leg and buttocks. When a disc herniation at the L5-S1 level compresses or inflames these roots, it can disrupt their function. Leading to the characteristic pain, weakness, or numbness known as sciatica.
Classic Symptoms of L5-S1 Disc Herniation
While many spinal conditions can cause general lower back pain, an L5-S1 herniation typically produces a distinct and often unmistakable pattern of discomfort that radiates down the leg. Recognizing these hallmark signs is the first step toward identifying the cause and pursuing effective treatment.
The Hallmarks of Sciatica: Pain in the Leg and Buttocks
Sciatica is, without question, the most common and debilitating symptom of an L5-S1 herniation. It is not a diagnosis itself but rather a descriptive term for pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve.
When the L5 or S1 nerve roots are compressed or chemically irritated by herniated disc material, the resulting pain may range from a dull ache to a sharp, electric-shock sensation.
Typical sciatica pain patterns include:
L5 nerve root compression: Pain, numbness, or tingling radiates along the outer thigh, across the knee, and into the top of the foot or big toe. When affected by a herniated disc, the L5 root causes back pain that extends into the buttock, lateral thigh, lateral calf, dorsum of the foot, and big toe. Muscle weakness may occur in hip abduction, knee flexion, foot dorsiflexion, and big toe dorsiflexion.
S1 nerve root compression: Pain extends from the buttock down the back of the thigh and calf, often involving the ankle and sole of the foot. S1 compression produces sacral or buttock pain radiating into the posterolateral thigh, calf, and lateral or plantar foot. Associated findings include weakness in plantar flexion and a diminished Achilles reflex.
In more severe cases, even simple activities: such as sitting, standing, or walking for short periods. It can become intensely painful, greatly restricting mobility and quality of life.

Other Key Indicators of L5-S1 Issues
Beyond the radiating pain of sciatica, an L5-S1 herniation can present with several additional symptoms that reflect the extent of nerve root involvement:
Foot drop or muscle weakness: Compression of the L5 nerve root can weaken the muscles responsible for lifting the foot (dorsiflexion), leading to a condition known as foot drop. Similarly, involvement of the S1 root can impair the muscles used for pushing off during walking (plantar flexion), making activities like walking or climbing stairs difficult.
Paresthesia (numbness and tingling): Persistent pressure on the affected nerve disrupts normal signal transmission, causing chronic numbness, tingling, or “pins and needles” sensations. These sensory changes typically follow the specific dermatome associated with the compressed nerve root.
Reflex changes: During a physical examination, a clinician may detect a reduced or absent Achilles tendon reflex, a hallmark sign of S1 nerve root compression.
Looking for a Second Opinion?
Upload your MRI for a free review and consultation with leading spine surgeon Dr. Ara Deukmedjian, and discover a proven solution for your back pain. Instead of continuing to struggle with your symptoms, take the step to fix your back pain for good.
When to Suspect Cauda Equina Syndrome (A Serious Warning)
It is crucial to be aware of a rare but urgent complication that can occur with a large disc herniation, particularly at the L5-S1 level: cauda equina syndrome (CES). The cauda equina (Latin for “horse’s tail”) is a bundle of nerves located below the L1–L2 level, and massive compression of these nerves is a true surgical emergency.
If you experience any of the following, seek immediate medical attention:
- Sudden or progressive loss of bladder or bowel control (incontinence).
- Saddle anesthesia: severe numbness or tingling in the “saddle area” (inner thighs, buttocks, and groin).
- Severe weakness in both legs.
While cauda equina syndrome is exceedingly rare, these symptoms demand urgent treatment to reduce the risk of permanent paralysis or long-term disability.
Investigating the Connection: L5-S1, The Gut, and Referred Abdominal Pain
The question of whether an L5-S1 herniation can cause stomach or digestive problems is a common source of confusion for patients. While the core medical consensus is that the herniation itself does not directly cause conditions like ulcers or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), symptoms such as referred abdominal pain, bloating, or constipation can still occur in some individuals and are clinically recognized as a complex, indirect consequence of the spinal problem.
Why Abdominal Pain is NOT a Typical Symptom of L5-S1
To be clear, the nerves that regulate the gastrointestinal system (digestion, motility, organ function) are part of the autonomic nervous system. These nerves originate at different levels of the spine. Primarily the thoracic and upper lumbar regions and are distinct from the somatic L5 and S1 nerve roots that control leg movement and sensation.
Therefore, there is no direct, validated anatomical or physiological pathway by which a typical posterior L5-S1 disc herniation can cause a true digestive disorder. A bulging disc that protrudes backward into the spinal canal cannot directly cause stomach gas or alter the chemical environment of your gut.
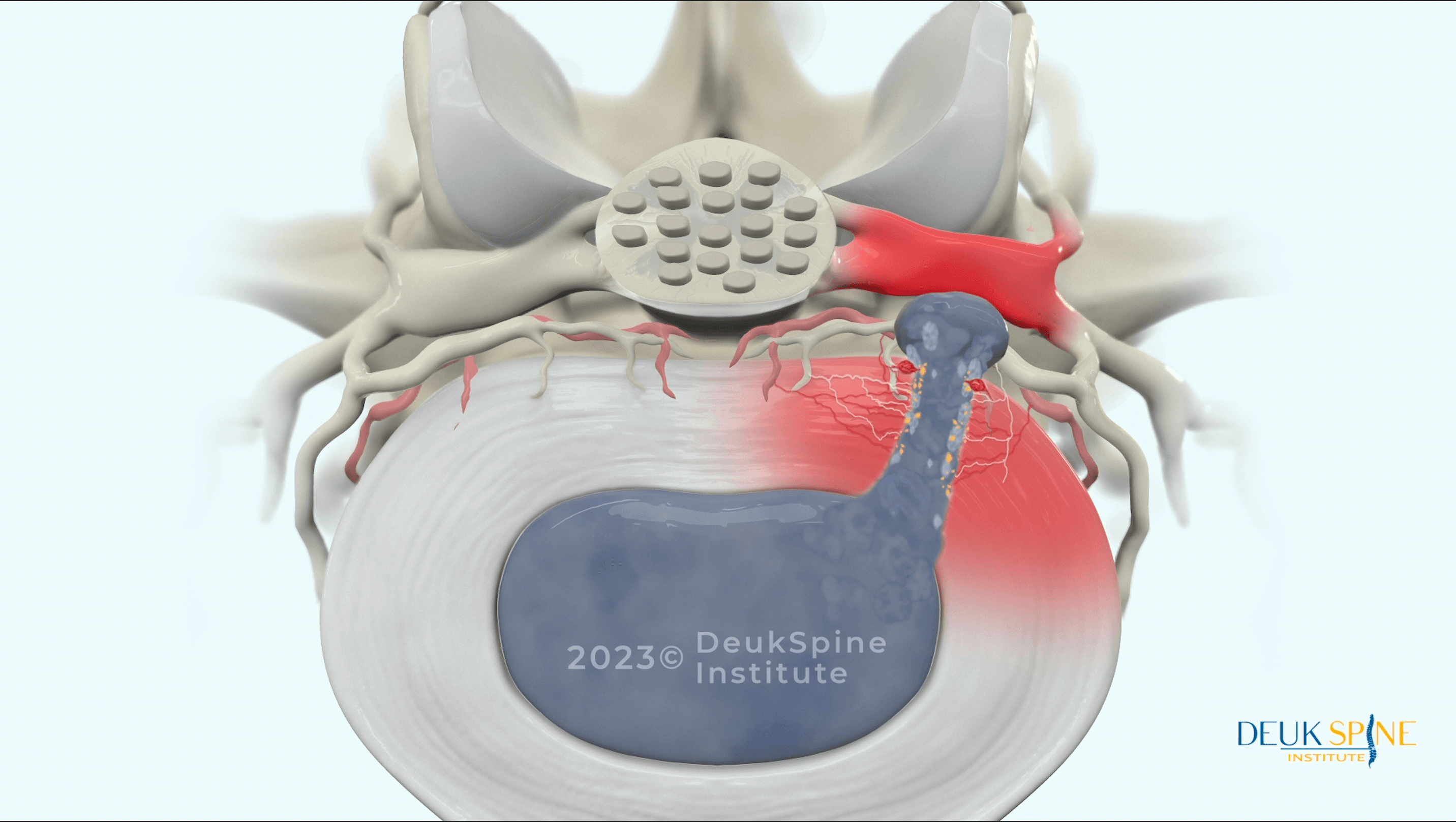
The Exception: Ventral Disc Herniations and the Superior Hypogastric Plexus
However, recent research has identified an important exception that helps explain why some patients experience genuine visceral pain from lumbar disc problems.
A groundbreaking case series published in a peer-reviewed medical journal documented that ventral (front-facing) disc herniations at L4-L5 or L5-S1 can cause direct physical trauma to the superior hypogastric plexus (SHP), a major sympathetic nerve structure located on the anterior (front) surface of the lumbar spine.3
The superior hypogastric plexus is part of the autonomic nervous system and provides sympathetic innervation to the pelvic organs. When a disc herniates anteriorly. Toward the front of the body rather than posteriorly toward the spinal canal. It can compress or irritate the SHP, causing:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Lower abdominal discomfort
- Pain with sexual intercourse
- Visceral pain patterns that do not respond to typical treatments
The researchers proposed that this mechanism creates a condition they termed “visceral complex regional pain syndrome,” in which sympathetic dysfunction maintains chronic visceral pain. In their case series, patients with documented ventral disc herniations at L5-S1 who had pelvic and abdominal pain experienced significant relief after superior hypogastric plexus blocks and, in some cases, after laser disc ablation directly targeting the herniation.
This represents a rare but important mechanism by which L5-S1 disc pathology can cause genuine abdominal and pelvic pain and not through the typical posterior herniation compressing spinal nerve roots, but via anterior herniation compressing autonomic sympathetic structures.
Understanding Referred Abdominal Pain in Spinal Conditions
For more common posterior disc herniations, when patients notice abdominal sensations, the explanation often lies in the phenomenon of referred pain. Referred pain occurs when the brain misinterprets pain signals that originate in one part of the body as coming from another, due to the complex way different nerve pathways converge as they enter the spinal cord. A process known as neural convergence.
Recent research on referred pain mechanisms published in 2023 describes how dichotomizing afferent fibers branch and distribute to both the primary site of dysfunction and distant referred areas. Using double-labeling with fluorescent tracers, investigators have demonstrated dichotomizing axons running between the lumbar intervertebral disc and the groin region, providing concrete anatomical evidence for these referral patterns.4
The authors note that “referred pain related to lumbar spine diseases tends to spread to the lower abdomen, groin, and pelvic regions,” and that when primary spinal lesions stimulate deep afferent fibers, these inputs can activate a reflex arc that produces pain perception in remote locations.
Building on this, a 2024 systematic review of pain pathophysiology reported that the autonomic and emotionally unpleasant aspects of pain are transmitted to the medial thalamus via the medial spinothalamic tract, helping explain how spinal pathology can generate visceral-like sensations; such as abdominal discomfort and even when no gastrointestinal organ is directly involved.5
In rare cases of L5-S1 herniation, especially large ones that push forward or laterally, the irritation can be deep enough to activate these referred pain pathways. The discomfort is not caused by the stomach itself, but rather by the irritated nerves of the lumbosacral plexus near the spine. In effect, the spinal problem generates a painful signal that the brain misinterprets as coming from the front of the body.
This is a crucial distinction: the source of the pain remains the spine, not a visceral organ.
Indirect Causes: Posture, Stress, and Secondary Digestive Issues
The most common explanation for gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in people with chronic lower back pain usually does not involve direct nerve damage, but rather the indirect consequences of living in constant pain.
Altered posture and guarding: Patients often subconsciously adopt “guarding” behaviors, such as holding the body stiffly to avoid movements that trigger pain. This altered posture—combined with changes in core muscle activation and shallower, restricted breathing—can mechanically increase pressure on the abdomen, creating sensations of tightness, pressure, or mild pain that may be perceived as bloating.
Reduced mobility: Chronic pain frequently leads to a sedentary lifestyle. Low levels of physical activity are a well-established contributor to slower digestion and constipation, further aggravating GI discomfort.
Stress and autonomic dysfunction: Research on the autonomic nervous system in chronic pain shows that ongoing pain acts as a major physiological stressor.6 This stress response elevates cortisol and inflammatory markers, which are known to negatively affect gut motility and to worsen pre‑existing GI sensitivities, resulting in more gas, bloating, and irregular bowel habits.
A 2025 review on central sensitization in chronic low back pain reported that symptoms persisting beyond 12 weeks are commonly associated with complex psychosocial difficulties, sleep problems, depression, and anxiety. All of these factors can disrupt autonomic nervous system balance and, in turn, influence digestive function and symptom severity.7
Effective symptom management requires acknowledging that these secondary GI issues, while not caused directly by the disc, are real consequences of untreated discogenic pain.
Patient Story: Relief After Years of Failed Treatments
Hear how this patient's lower back pain is finally gone after years of pain and injections that stopped working:
This patient's story illustrates a common pattern: conservative treatments like injections may provide temporary relief, but when symptoms persist or return, addressing the structural source of pain through advanced techniques like Deuk Laser Disc Repair® can provide permanent resolution.
Many patients with L5-S1 herniations experience a cycle of temporary relief from conservative care followed by symptom recurrence. Understanding when conservative treatment has been exhausted and more definitive intervention is needed is crucial for preventing permanent nerve damage and restoring quality of life.
Diagnosis and Conservative Symptom Management
The path to relief from an L5-S1 herniation begins with an accurate diagnosis, followed by a treatment plan tailored to the condition's severity. Most patients initially seek non-surgical treatment pathways.
The Role of MRI and Clinical Evaluation in Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis involves two primary components:
Clinical history and physical exam: A spine specialist will review your symptoms, their location, and the factors that aggravate and relieve them. They will perform maneuvers to test your muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation, helping them pinpoint which nerve root (L5 or S1) is involved.
High-quality MRI imaging: The MRI is the definitive tool. It allows the physician to visualize the soft tissues, confirm the presence and size of the L5-S1 herniation, assess the degree of nerve root compression, and identify the location and extent of the annular tear that causes discogenic pain. Without a detailed MRI, a precise and effective treatment plan is impossible.
A 2025 systematic review of treatment guidelines for lumbar disc herniation emphasized that imaging findings must be interpreted in clinical context and that unnecessary surgery is often performed when imaging abnormalities are treated without proper clinical correlation.8
Important consideration: MRI findings don't always correlate with symptoms. Many asymptomatic individuals have disc herniations visible on imaging. The key is correlating what the MRI shows with your specific clinical presentation.
Non-Surgical Treatment Pathways and Their Limitations
Conservative care is the standard first-line approach for an L5-S1 herniation unless red-flag symptoms are present. However, while these options may provide temporary symptom relief, they do not repair the underlying structural damage, such as an annular tear.
Physical therapy and exercise: Strengthening the core and improving flexibility can reduce stress on the L5-S1 segment. This is an excellent adjunct to treatment, but it cannot heal the annular tear or remove the herniated disc material.
Injections (epidural steroids): These injections deliver a potent anti-inflammatory medication directly to the area of nerve irritation. They can provide significant, but usually temporary relief by reducing inflammation, yet they do not correct the mechanical cause of the herniation.
Pain medications: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help control pain, but they do not address the underlying spinal problem. Long-term dependence on these medications carries risks of side effects and potential dependency.
For many patients with persistent sciatica or ongoing discogenic pain that does not improve after 6 to 12 weeks of conservative care. A more definitive treatment is often needed to achieve lasting relief.
Advanced Treatment: The Deuk Laser Disc Repair® Advantage
When conservative care fails to relieve chronic pain and restore quality of life, surgical intervention is often considered. However, traditional open spinal surgeries, such as spinal fusion or laminectomy, are associated with long recovery times, muscle damage, and a risk of failed back surgery syndrome.
Deuk Laser Disc Repair®, pioneered by Dr. Ara Deukmedjian at Deuk Spine Institute, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of herniated discs, offering a safer, less invasive, and more targeted alternative to conventional open surgery.
DLDR®
Watch this short video to understand how our minimally invasive technique relieves pain permanently.
A Minimally Invasive Solution for L5-S1 Herniations
Deuk Laser Disc Repair® is a state-of-the-art, minimally invasive, outpatient procedure specifically designed to treat the source of both discogenic pain and radicular symptoms such as sciatica.
Key steps and advantages of DLDR®:
Pinpoint accuracy: The procedure is performed through a tiny (7-millimeter) incision—the diameter of a pencil—using advanced endoscopic visualization that provides the surgeon with a magnified, clear view of the spine.
No cutting of bone: Unlike traditional surgery, DLDR does not cut through the bone or large muscles. This preserves spinal stability, dramatically reduces recovery time, and minimizes blood loss and post-operative pain.
Laser precision: A Holmium YAG laser is used to meticulously debride and vaporize the damaged disc tissue (the part causing the herniation) and remove inflammatory material from the annular tear. This direct removal of the damaged tissue is what provides immediate, lasting relief by decompressing the nerve root.
Preservation of function: The most significant advantage is that the procedure preserves disc function and spinal mobility. No screws, rods, or fusions are required, ensuring the spine remains healthy and flexible.
Unmatched safety record: With over 2,000 procedures performed, Deuk Laser Disc Repair® has a record of 99.6% success rate with zero complications.
Why DLDR is Superior to Spinal Fusion or Traditional Discectomy
Traditional spinal fusion permanently locks two or more vertebrae together, which can transfer stress to the adjacent discs and often lead to new problems over time. A traditional microdiscectomy is less destructive but still requires some bone removal and carries a higher risk of re‑herniation.
Deuk Laser Disc Repair® achieves superior outcomes by focusing solely on healing the damaged disc and relieving pressure without creating new issues:
Faster recovery: Patients are typically able to return to normal activities within days rather than weeks or months.
Elimination of discogenic pain: By precisely debriding the annular tear, the procedure directly targets and removes the source of deep discogenic pain.
Long‑term solution: By removing the herniated material and repairing the tear, the procedure is designed to provide lasting relief rather than temporary symptom control.
Choosing Deuk Laser Disc Repair® means opting for one of the safest and most effective ways to eliminate lower back pain and sciatica and regain control of your life.
Taking the Next Step Toward Permanent Pain Relief
The symptoms of an L5-S1 herniation from debilitating sciatica to confusing referred abdominal pain can severely affect both your physical and emotional well-being. While conservative treatments can help manage symptoms, they cannot permanently correct underlying structural damage.
If you are living with chronic lower back pain and radicular symptoms that have persisted for more than a few weeks, do not settle for temporary relief or ongoing discomfort. A lasting solution is available through the precision and safety of Deuk Laser Disc Repair®.
Take the first step toward a pain-free life today: click the banner and upload your MRI for a free review and consultation with Dr. Deukmedjian. And take the first step to living a pain-free life again.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can an L5-S1 herniation cause severe digestive problems like loss of bowel control?
A: Loss of bowel or bladder control is an extremely rare but severe red-flag symptom that may indicate Cauda Equina Syndrome, a serious condition requiring emergency care. It is caused by massive compression of the nerve roots, not by the disc directly causing a digestive illness. If you experience this, seek immediate medical attention.
Q: How long does recovery typically take after Deuk Laser Disc Repair® for an L5-S1 disc?
A: Deuk Laser Disc Repair® is an outpatient procedure, meaning you go home the same day. Most patients report immediate relief from sciatica and discogenic pain and can return to light activity within 1-3 days. Full recovery is significantly faster than with traditional surgery, often allowing a return to normal daily life within 1 to 2 weeks, depending on the severity of the prior condition.
Q: I only have mild lower back pain, but my sciatica is intense. Should I wait to seek treatment?
A: You should not wait. Intense sciatica is a sign of significant nerve root compression, even if the lower back pain (the discogenic pain) is mild. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent permanent nerve damage. If conservative care fails to resolve the severe sciatica within 6-8 weeks, consulting a specialist about advanced options such as Deuk Laser Disc Repair® is highly recommended to protect the nerve.
Q: What is the difference between referred abdominal pain caused by the spine and true organ-related pain?
A: Referred abdominal pain from the spine is typically positional; it is often worsened by specific movements (like bending forward or twisting), prolonged sitting, or coughing/sneezing. True organ-related pain (visceral pain) is usually associated with digestive function (eating, fasting, bowel movements) and is often accompanied by other GI symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or fever. Always consult a physician to properly differentiate the cause of the pain.
Q: Can a ventral disc herniation really cause abdominal pain?
A: Yes. Research published in 2023 documented that ventral (front-facing) disc herniations at L4-L5 or L5-S1 can compress the superior hypogastric plexus, a sympathetic nerve structure on the anterior spine, causing genuine pelvic and abdominal pain. This is different from typical posterior disc herniations. Patients with this rare presentation may experience relief from superior hypogastric plexus blocks or direct treatment of the herniation.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
- https://jhwcr.com/index.php/jhwcr/article/download/541/364
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4478827/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10338069/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11581984/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11765779/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10871156/
- https://www.e-neurospine.org/journal/view.php?number=1714