By Dr. Ara Deukmedjian, MD
Board-Certified Neurosurgeon, Deuk Spine Institute
Medically reviewed on February 18, 2026
Medical disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Individual results may vary. Always consult with your healthcare provider about your specific condition and treatment options.
Key Points
✓ Herniated discs are extremely common - Annual incidence is 5-20 cases per 1,000 adults with lifetime prevalence up to 43%
✓ Most improve without surgery - 75% of patients experience significant improvement within one month with conservative care
✓ Inflammation drives pain, not just compression - The primary source of pain is inflammatory chemicals from the nucleus pulposus
✓ Spontaneous resorption occurs - Herniated disc material can naturally shrink over 3-6 months in many cases
✓ MRI is the diagnostic gold standard - X-rays and CT scans cannot accurately visualize disc herniations
✓ Timing of surgery matters - Longer symptom duration correlates with worse surgical outcomes and lower neurologic recovery
✓ Conservative treatment works for most - Surgery is only necessary when conservative care fails or neurological deficits progress
✓ Traditional surgery has limitations - 25-33% of microdiscectomy patients report poor outcomes
✓ Minimally invasive options exist - Deuk Laser Disc Repair has 99.6% success rate with zero complications
✓ Cauda equina syndrome is an emergency - Sudden bowel/bladder dysfunction requires immediate medical attention
Understanding Herniated Discs: What's Really Happening in Your Spine
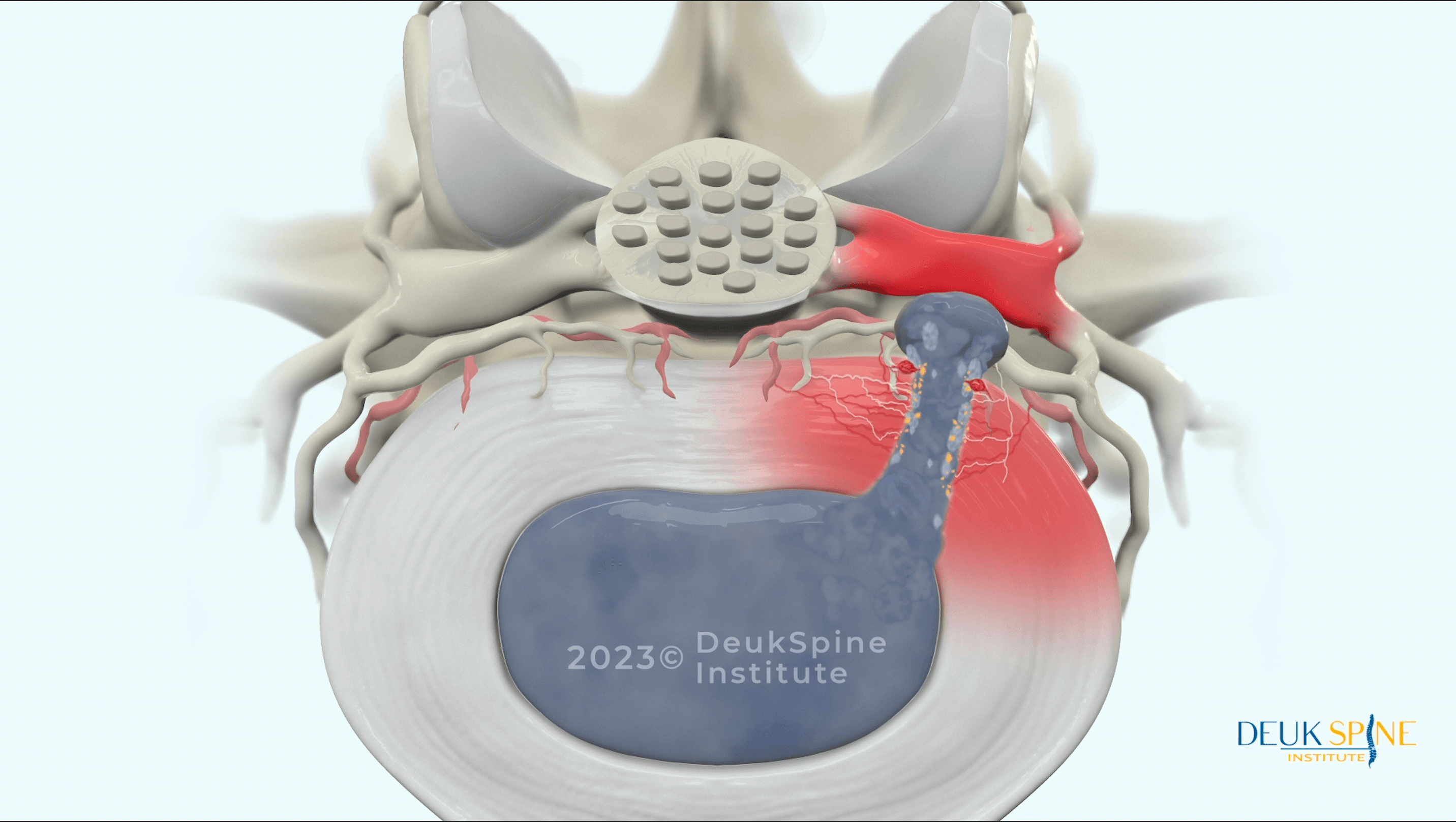
A herniated disc is an injured intervertebral disc. To understand what this means, it helps to first understand basic disc anatomy.
Your spine contains 23 intervertebral discs positioned between the vertebrae, acting as natural shock absorbers. Each disc has two main parts:
Annulus fibrosus: The tough outer ring made of concentric layers of collagen fibers arranged in a crisscross pattern. This structure provides strength and stability.
Nucleus pulposus: The soft, gel-like inner core that cushions the spine and helps distribute pressure.
The Herniation Process
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner core pushes through a tear in the tough outer layer. This process typically begins with trauma to the annular ring, which can lead to a cascade of degenerative changes.
Recent research has clarified the stages of disc pathology:
- Annular tear: The outer ring develops small tears, often from trauma, repetitive stress, or age-related degeneration
- Disc bulging: The entire disc circumference extends beyond its normal boundaries
- Disc protrusion: A focal area of the disc pushes outward but remains contained by the outer annulus
- Disc extrusion: The nucleus pulposus breaks completely through the annulus and extends into the spinal canal
- Disc sequestration: A fragment of disc material completely separates and becomes free-floating
- Spondylosis: Advanced degeneration affects both the disc and vertebral endplates, appearing as arthritis
The Real Source of Pain: Inflammation
Here's what many patients and even some physicians don't fully appreciate: the primary source of pain from a herniated disc is not mechanical compression of nerves, but rather inflammation caused by nucleus pulposus fragments within the posterior annular tear.
When disc material herniates and comes into contact with surrounding tissues, it triggers an intense inflammatory response. The nucleus pulposus contains inflammatory substances including:
- Phospholipase A2
- Prostaglandins
- Cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-6
- Matrix metalloproteases
These chemical irritants sensitize nearby nerve roots, creating pain even without significant mechanical compression. A 2025 study examining inflammation in intervertebral disc herniation confirmed that inflammatory cytokines play a critical role in generating the pain associated with disc herniation. 1
This understanding is crucial because it explains why simply removing mechanical pressure (through traditional discectomy) doesn't always eliminate pain. The inflammatory annular tear must also be addressed.
How Common Are Herniated Discs?
Herniated discs are remarkably prevalent. Research shows that the annual incidence of sciatica (the most common symptom of lumbar disc herniation) is 1-5% of the general population, with overall lifetime prevalence as high as 43%.
A 2023 study examining the epidemiology of lumbar disc herniation found that the annual incidence ranges from 5 to 20 cases per 1,000 adults in the United States.
Importantly, not all disc herniations cause symptoms. Studies consistently show that many asymptomatic individuals have disc herniations visible on MRI. What matters is whether your specific herniation correlates with your symptoms.
Symptoms of Herniated Discs
The symptoms of a herniated disc vary significantly depending on its location and severity. Understanding these patterns helps with accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.

Lumbar (Lower Back) Herniated Disc Symptoms
A herniated disc in the lumbar spine often causes lower back pain that can worsen with movement, bending, twisting, or sitting for long periods. However, the most recognizable symptom is sciatica.
Sciatica: The Hallmark of Lumbar Disc Herniation
Sciatica is a sharp, radiating pain that follows the path of the sciatic nerve. From the lower back through the buttock and down the leg. The exact pain pattern depends on which nerve root is affected:
L4–L5 Disc Herniation
- Pain down the outer thigh and leg
- Numbness or tingling on the top of the foot and big toe
- Weakness lifting the foot upward
- Trouble walking on the heels
L5–S1 Disc Herniation
- Pain down the back of the thigh and calf
- Numbness or tingling on the bottom of the foot and outer toes
- Weakness when pushing up on the tiptoes
- Reduced or absent Achilles tendon reflex
Additional Lumbar Herniation Symptoms
- Leg weakness
- Numbness or “pins and needles” sensations
- Lower back muscle spasms
- Pain that worsens with coughing, sneezing, or straining
- Difficulty standing or walking for long periods
Cervical (Neck) Herniated Disc Symptoms
A herniated disc in the cervical spine causes neck pain that may worsen with certain head movements or positions. However, just like lumbar herniations, the most significant symptoms come from nerve compression.
Cervical Radiculopathy: Arm Pain Caused by Neck Problems
It’s important to understand that neck pain alone is not caused by a pinched nerve. Instead, compression of a cervical nerve root leads to arm pain, weakness, or numbness; a condition known as cervical radiculopathy.
The exact symptoms depend on which cervical nerve root is affected:
C5–C6 Disc Herniation
- Pain radiating into the thumb and index finger
- Weakness in the biceps
- Numbness along the thumb side of the hand
C6–C7 Disc Herniation
- Pain radiating into the middle fingers
- Weakness in the triceps and wrist extensors
- Numbness in the middle fingers
Additional Cervical Herniation Symptoms
- Headaches, especially at the base of the skull
- Shoulder pain
- Upper back pain between the shoulder blades
- Weakness or clumsiness in the hands
- Difficulty with fine motor tasks (e.g., buttoning clothes, writing)
When Symptoms Indicate an Emergency
While most herniated discs cause painful but non-urgent symptoms, some warning signs indicate a medical emergency and require immediate attention.
Cauda Equina Syndrome: A Rare but Serious Emergency
Cauda equina syndrome occurs when a large disc herniation compresses multiple nerve roots in the lower spine. This can lead to severe, rapidly worsening neurological problems, including:
- Sudden loss of bowel or bladder control
- Saddle anesthesia (numbness in the groin, inner thighs, or buttocks)
- Severe weakness in both legs
- Increasing numbness or tingling in the legs
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek emergency medical care right away. Cauda equina syndrome requires urgent surgical decompression to prevent permanent paralysis and loss of bowel or bladder function.
Causes and Risk Factors for Herniated Discs
Understanding what causes disc herniations can help you prevent them or make informed decisions about treatment.
Primary Causes
Trauma and Acute Injury:
A herniated disc often results from physical strain or sudden injury. Trauma, improper lifting (especially while twisting), high-impact falls, or motor vehicle accidents can cause immediate disc damage. The sudden force can overwhelm the disc’s structure, creating tears in the annulus fibrosus.
Degenerative Changes:
Age-related degeneration is the most common underlying cause. As discs age, they naturally lose water content. A process called desiccation; which makes them less flexible and more vulnerable to tearing. Over time, small annular tears accumulate, weakening the disc and increasing the likelihood of herniation even with minor stress.
Repetitive Stress:
Jobs or activities that involve frequent bending, lifting, or twisting can create cumulative wear on the discs. While each individual movement may be harmless, thousands of repetitions gradually weaken the annulus fibrosus, making herniation more likely.
Significant Risk Factors
Age:
Age is the most important risk factor. As spinal discs lose water content and flexibility over time, they become more prone to tearing. Lumbar disc herniations most commonly occur between ages 30–50, when discs have already lost significant hydration but people remain physically active.
Occupation and Physical Activity:
Repetitive physical strain such as bending, lifting, or twisting significantly increases the risk of herniation. Jobs that involve heavy manual labor, long periods of driving with whole-body vibration, or frequent forward bending place excessive stress on the lumbar discs.
Obesity:
Excess body weight puts continuous pressure on the spine and accelerates disc degeneration. Research clearly shows a connection between higher BMI and a greater likelihood of disc herniation.
Sedentary Lifestyle:
Lack of physical activity is another risk factor. A sedentary lifestyle weakens the muscles that support the spine, which increases reliance on the discs and ligaments. Prolonged sitting also increases intradiscal pressure by up to 40 percent compared to standing.
Poor Posture:
Chronic poor posture, especially forward-leaning positions, creates abnormal and sustained loading on the discs. Over time, this uneven stress contributes to degenerative tears.
Genetic Predisposition:
A family history of disc problems raises individual susceptibility. Some people inherit tendencies toward earlier disc degeneration, weaker disc tissue, or abnormal spinal biomechanics.
Smoking:
Nicotine decreases blood flow to the spinal discs, which limits nutrient delivery and waste removal. This accelerates degeneration and reduces the disc’s ability to repair small areas of damage.
Potential Complications of Untreated Herniated Discs
While many herniated discs improve with conservative treatment, leaving certain cases untreated can lead to serious long-term problems.
Chronic Pain Syndromes
Persistent inflammation from an untreated herniated disc can lead to chronic pain that becomes harder to treat over time. As the condition progresses, the nervous system may become sensitized, a process known as central sensitization, in which pain signals are amplified and continue even after the original injury has partially healed.
Neurological Deficits
Long-term nerve compression can lead to a gradual loss of sensation or mobility in the affected extremities. When nerves remain compressed for extended periods, they may develop permanent damage that does not fully recover even after successful decompression.
Motor weakness: Prolonged compression can cause muscle atrophy (wasting away) in the legs or arms. Once significant atrophy occurs, full strength may not return.
Sensory loss: Permanent numbness or altered sensation can develop in areas supplied by the compressed nerve.
Accurate Diagnosis: The Foundation of Effective Treatment
The most effective way to diagnose a herniated disc is through a combination of expert clinical examination and advanced imaging, primarily MRI scans. Together, these tools can accurately identify the source of back and neck pain.
Clinical Examination
A comprehensive physical examination by an experienced spine specialist includes:
Medical history: Detailed discussion of symptom onset, character, location, aggravating and relieving factors
Range of motion testing: Assessment of how the spine moves and which movements reproduce symptoms
Neurological examination: Testing strength, sensation, and reflexes to identify which nerve roots are affected
Provocative tests: Specific maneuvers like the straight leg raise test or Spurling's test that help localize the problem
Imaging Studies
MRI: The Gold Standard
MRI is the most accurate method for diagnosing herniated discs. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, which primarily show bone structures, MRI can clearly visualize the soft tissues of the spine. It identifies the exact location and size of a herniation, evaluates the degree of nerve root compression, and reveals inflammatory changes in surrounding tissues.
A comprehensive 2025 systematic review of lumbar disc herniation treatment guidelines emphasized that imaging findings must always be interpreted in the proper clinical context, and that imaging alone cannot determine the true source of pain. 2
It is also important to note that many people without symptoms show disc herniations on MRI. The key is matching the imaging findings with the patient’s clinical presentation.
X-rays: Limited Value
X-rays visualize bone structures but cannot show disc herniations. They may reveal indirect signs, such as decreased disc space height or bone spurs, but they cannot accurately diagnose the specific disc problem.
CT Scans: Better Than X-rays but Inferior to MRI
CT scans offer better soft tissue detail than X-rays and provide excellent visualization of bone. However, they remain less accurate than MRI for diagnosing disc herniations.
Discography: Outdated and Unnecessary
Some clinicians still use discography, an invasive procedure in which dye is injected into the disc to see if it reproduces the patient’s pain. This test can cause discomfort, carries a risk of infection, and may even accelerate disc degeneration. With the high-quality imaging capabilities of modern MRI, discography is rarely needed today.
Free Expert MRI Review
Deuk Spine Institute offers a free MRI review, providing patients with an expert analysis to determine their pain generators with 99% diagnostic accuracy, without unnecessary appointments or expenses. This service has helped thousands of patients get accurate diagnoses and avoid inappropriate treatments.
Looking for Expert Diagnosis?
Treatment Options: From Conservative Care to Advanced Surgery
Treatment for herniated discs exists on a spectrum from conservative (non-surgical) approaches to surgical intervention. Understanding all options empowers you to make informed decisions.
Conservative Treatment: The First Line of Defense
For most patients with herniated discs, an initial trial of conservative treatment is appropriate. Recent research shows that 75% of patients with acute symptoms report marked improvement within one month. 3
Moreover, a groundbreaking 2025 study on spontaneous disc resorption found that herniated disc material can naturally shrink over time. The average duration of spontaneous resorption is between 3 and 6 months, with larger extrusions more likely to resorb than contained protrusions. 4
Medications for Symptom Management
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
Medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen can temporarily reduce inflammation and pain. However, they don't address the underlying cause of pain and long-term use carries risks.
Limitations: NSAIDs may cause gastrointestinal toxicities (ulcers, bleeding), cardiovascular issues (increased risk of heart attack and stroke), and kidney problems. They provide temporary relief but do nothing to prevent further disc damage.
Muscle Relaxants:
Medications like cyclobenzaprine may relieve muscle spasms but often cause drowsiness and dependency. They're typically used only short-term during acute pain episodes.
Corticosteroid Injections:
Epidural steroid injections deliver powerful anti-inflammatory medication directly to the area of nerve compression. They sometimes provide short-term relief (weeks to months), but frequent use may weaken spinal structures and cause bone loss.
Important reality: These medications fail to cure the root cause and can do more harm than good in the long run. They're tools for managing symptoms, not solutions for healing the disc.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Structured physical therapy can be highly effective for appropriate candidates. A comprehensive program includes:
Core strengthening: Building strength in abdominal and back muscles to support the spine
Flexibility training: Gentle stretching to maintain range of motion
Posture correction: Learning proper body mechanics
Aerobic conditioning: Low-impact cardiovascular exercise to promote healing
However, a 2024 study examining predictors of microdiscectomy outcomes found an interesting and unexpected result: participation in preoperative physical therapy was actually correlated with failure to meet minimal clinically important improvement thresholds after surgery. 5
This doesn't mean physical therapy is harmful, but it suggests that for patients with high-grade herniations destined for surgery, prolonged PT may simply delay necessary intervention without improving outcomes.
When Conservative Treatment Fails
Conservative treatment should be given an adequate trial (typically 6-12 weeks) before considering surgery. However, surgery should be considered sooner if:
- Symptoms are progressively worsening rather than improving
- Neurological deficits develop (weakness, numbness)
- Pain is so severe it prevents sleep or basic function
- Cauda equina syndrome develops (immediate emergency)
A 2024 German study on timing of surgery found that longer symptom duration correlates with worse outcomes and lower chances of neurologic recovery. Motor deficit recovery ranges from 33% to 75% depending on timing and treatment modality.
This research emphasizes that while conservative care should be tried first, unnecessary delays in surgery when it's truly needed can result in permanent damage.
Surgical Options: Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations
When conservative treatment fails, surgical intervention becomes necessary. However, not all surgical procedures are equal.
Microdiscectomy: The Traditional Standard
Microdiscectomy is the most commonly performed surgery for herniated discs. More than 300,000 are performed annually in the United States. The procedure involves:
- Accessing the spine through a 1-2 inch incision
- Removing a portion of the lamina (bone) to access the disc
- Removing the herniated portion of disc material
- Decompressing the compressed nerve root
The Problem with Microdiscectomy:
While microdiscectomy can relieve leg pain from nerve compression, 25-33% of patients report poor surgical outcomes.
Why? Because microdiscectomy does not treat discogenic back pain. The procedure removes the herniated material compressing the nerve, but it doesn't address the inflammatory annular tear that generates deep, aching back pain.
Additional limitations include:
- Requires cutting through muscle and removing bone
- Hospital stay of 1-2 days typically required
- Recovery period of 6-12 weeks
- Risk of recurrent herniation (5-15% of cases)
- Doesn't prevent future degeneration
- May create instability requiring fusion
Spinal Fusion: An Outdated Approach for Most Disc Problems
Some surgeons recommend spinal fusion for disc problems, particularly when multiple levels are affected or when they believe instability exists. Fusion permanently joins two or more vertebrae using screws, rods, and bone grafts.
However, fusion comes with severe drawbacks:
- Permanent loss of motion at the fused segment
- 11-36% risk of adjacent segment disease (accelerated degeneration at levels next to the fusion)
- Extended recovery (6-12 months)
- Hardware complications
- Higher complication rates than motion-preserving procedures
For most herniated discs, fusion is unnecessary and potentially harmful. Disc problems rarely require fusion unless structural instability is present.
The Superior Alternative: Deuk Laser Disc Repair
Deuk Laser Disc Repair® (DLDR) is a revolutionary, minimally invasive procedure designed to treat herniated discs without spinal fusion, large incisions, or artificial disc implants.
How Deuk Laser Disc Repair Works
The procedure uses advanced endoscopic and laser technology to address both the herniated material and the inflammatory annular tear:
- Tiny incision: A 4-7mm incision (smaller than a pencil eraser) is made
- Endoscopic access: A specialized tubular retractor creates a pathway to the disc
- High-definition visualization: An endoscopic camera provides magnified views
- Laser precision: A Holmium:YAG surgical laser removes only the damaged, inflammatory disc tissue
- Annular tear debridement: The laser treats the painful annular tear, eliminating the source of discogenic pain
- Preservation of healthy tissue: The healthy portion of the disc remains intact
Why Deuk Laser Disc Repair Is Superior
Treats Both Problems:
Unlike microdiscectomy that only addresses nerve compression, DLDR treats both the herniation and the inflammatory annular tear, eliminating both leg pain and back pain.
Truly Minimally Invasive:
- 4-7mm incision (not the 1-inch or larger cuts of "minimally invasive" fusion)
- No bone removal
- No muscle cutting
- No hardware placement
Exceptional Safety and Success:
- 99.6% success rate in eliminating disc-related pain
- Zero complications in over 2,000 procedures performed over 15 years
- Published in peer-reviewed medical journals
Rapid Recovery:
- Outpatient procedure (go home the same day)
- Walking within an hour
- Return to desk work within 3-5 days
- Full recovery within 2-3 weeks
- No postoperative narcotics needed
Motion Preservation:
- No fusion means your spine maintains natural motion permanently
- No risk of adjacent segment disease
- Can return to all activities without restrictions
Proven Technique:
The procedure has been published in Surgical Neurology International and other peer-reviewed journals, documenting its safety and effectiveness.
Patient Story: From Chronic Pain to Complete Relief
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can a herniated disc heal on its own without surgery?
A: Yes, many herniated discs improve significantly without surgical intervention. Research shows that 75% of patients with acute symptoms experience marked improvement within one month. Furthermore, recent studies on spontaneous disc resorption demonstrate that herniated disc material can naturally shrink over 3-6 months as the immune system recognizes and removes it. However, "healing" doesn't mean the disc returns to its original state. The annular tears remain, but symptoms often resolve as inflammation subsides. If symptoms don't improve within 6-12 weeks of appropriate conservative care or if neurological deficits develop, surgical evaluation is warranted.
Q: How long should I try conservative treatment before considering surgery?
A: For most patients, an adequate trial of conservative treatment is 6-12 weeks. This should include appropriate medications, physical therapy, activity modification, and potentially epidural injections. However, surgery should be considered sooner if you experience progressive weakness, severe unrelenting pain that prevents sleep or basic function, or signs of cauda equina syndrome. A 2024 study found that longer symptom duration correlates with worse surgical outcomes and lower neurologic recovery rates. This means while conservative care should be tried first, unnecessarily delaying surgery when it's truly needed can result in permanent nerve damage.
Q: What's the difference between a herniated disc and a bulging disc?
A: Both represent disc pathology but differ in severity. A bulging disc occurs when the entire disc circumference extends beyond the vertebral margins, but the outer annulus remains intact. It's like a tire bulging but not yet flat. A herniated disc (also called disc extrusion) occurs when the outer annulus develops a complete tear, allowing the inner nucleus pulposus to leak out into the spinal canal. Herniated discs are more likely to cause severe, acute symptoms because the extruded material is highly inflammatory. However, from a treatment perspective at Deuk Spine Institute, both can be effectively treated with motion-preserving procedures like Deuk Laser Disc Repair® when they cause symptoms.