By Dr. Ara Deukmedjian, MD
Board-Certified Neurosurgeon, Deuk Spine Institute
Medically reviewed on February 12, 2026
Medical disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Individual results may vary. Always consult with your healthcare provider about your specific condition and treatment options.
Key Points
✓ Herniated discs are common — Lumbar disc herniation affects 5–20 adults per 1,000 each year, making it a leading cause of back pain and sciatica.1
✓ Inflammation drives most pain — Not just nerve compression; symptoms are largely caused by inflammatory chemicals released when nucleus pulposus material leaks through an annular tear.
✓ Certain levels are affected most — L4–L5 and L5–S1 account for roughly 95% of all lumbar disc herniations.
✓ Exercise therapy works — A 2025 meta-analysis in Frontiers in Medicine showed significant reductions in pain and disability, plus improved quality of life.
✓ Conservative care helps many patients — A medical publication review in 2024 confirmed that most people improve without surgery; surgical intervention is mainly for progressive neurological symptoms or failed conservative treatment.
✓ Minimally invasive options are advancing — Procedures like Deuk Laser Disc Repair® removes the herniated material without fusion, bone removal, or long recovery times.
✓ Accurate diagnosis is essential — A combination of clinical exam and MRI findings is critical to prevent nerve damage and select the best treatment path.
✓ Know the red flags — Sudden loss of bladder or bowel control requires emergency evaluation for possible cauda equina syndrome.
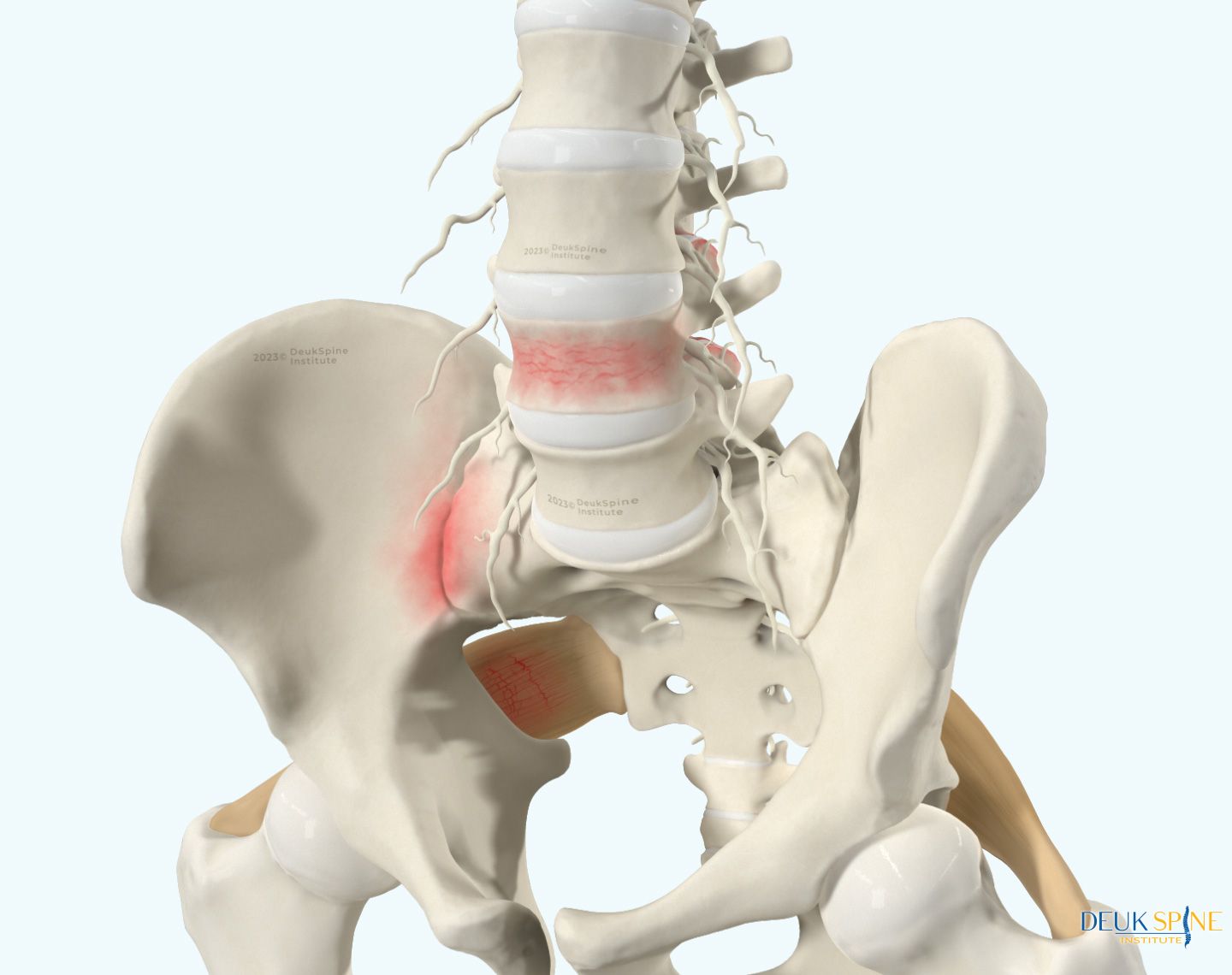
What Is a Herniated Disc in the Lower Back?
A herniated disc in the lower back is among the most prevalent and debilitating spinal conditions in adults. It occurs when the soft, gel-like inner core of an intervertebral disc. Called the nucleus pulposus that pushes through a tear in the tough outer ring, the annulus fibrosus, into the spinal canal or neural foramen. This leakage triggers an intense inflammatory response that irritates nearby spinal nerves, resulting in the sharp, burning, or radiating pain that most patients experience.
Often described as a “slipped disc” or “ruptured disc,” a lumbar disc herniation most commonly occurs at the L4-L5 and L5-S1 vertebral levels, which bear the greatest mechanical stress during everyday movements, such as bending and lifting. Between 60 and 80 percent of adults will experience low back pain during their lifetime, and a significant portion of those cases involve disc herniation.
At Deuk Spine Institute, board-certified neurosurgeon Dr. Ara Deukmedjian and his team have treated thousands of patients with lumbar disc herniation using a comprehensive, patient-centered approach from conservative management to the advanced, minimally invasive Deuk Laser Disc Repair®. This guide explains everything you need to know about herniated discs in the lower back, grounded in the latest medical research.
Anatomy of the Lower Back: Why Discs Herniate
Your lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae (L1–L5) stacked on top of one another, connected by intervertebral discs that function as shock absorbers. Each disc has two essential components:
Annulus fibrosus: The tough, fibrous outer wall composed of 15–25 concentric collagen layers that contain and support the nucleus pulposus.
Nucleus pulposus: The soft, hydrated, gel-like inner core (approximately 80% water) that absorbs compression during movement, bending, and lifting.
The L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels bear the most mechanical stress and account for approximately 95% of all lumbar disc herniations. These two levels connect the flexible lumbar spine to the more rigid sacrum, exposing them to repeated strain and degeneration over time.
A critical insight: pain is primarily caused by inflammation, not just nerve pinching. When disc material leaks through an annular tear, it releases inflammatory chemicals that irritate the sensory nerves embedded in the outer annulus and the adjacent nerve roots. This is why two patients with identical MRI findings can have vastly different pain levels.
Causes and Risk Factors of Lumbar Disc Herniation
Disc herniation arises from a combination of degenerative, mechanical, and lifestyle factors. Understanding the underlying causes helps patients reduce future injury risk and make informed treatment decisions.
Age-Related Disc Degeneration
As we age, intervertebral discs gradually lose their water content and elasticity. The nucleus pulposus becomes less hydrated and more fibrous, while the annulus fibrosus develops microscopic fissures. This degeneration makes the disc more vulnerable to herniation, even from minor stress. Most disc herniations occur in people in their 30s and 40s when the nucleus is still gel-like and capable of extrusion.
Trauma and Acute Injury
Sudden, forceful impact such as a fall, car accident, or heavy lifting with poor form. Can cause an annular tear and disc herniation. Repetitive mechanical stress, such as jobs requiring frequent bending, twisting, or heavy lifting, also significantly increases herniation risk.
Lifestyle and Modifiable Risk Factors
Modifiable risk factors supported by current research include:
- Obesity: A 2024 study found that individuals with a BMI above 30 have significantly higher risk of lumbar disc herniation compared to those with normal BMI due to increased load on the lumbar spine.
- Smoking: Tobacco use reduces disc blood supply and accelerates degeneration. A 2022 systematic review confirmed the link between smoking and degenerative spinal disease.2
- Physical inactivity: Weak core muscles fail to adequately support the lumbar spine, increasing disc stress.
- Prolonged sitting and poor posture: Sustained flexion dramatically increases intradiscal pressure and hastens annular degeneration.
- Genetics: Mutations in collagen genes (COL1A1, COL9A2) and matrix metalloproteinase genes have been linked to accelerated disc degeneration.
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc in the Lower Back
Symptoms depend on which disc is herniated, which nerve root is affected, and the severity of inflammation and compression. Some individuals with lumbar disc herniations visible on MRI experience no symptoms at all underscoring that imaging findings must always be interpreted alongside clinical evaluation.
Lower Back Pain
Localized lower back pain, ranging from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations, is often the first sign. Pain typically worsens with bending forward, prolonged sitting, coughing, or sneezing. Muscle spasms may develop as the body instinctively tries to protect the injured segment.
Sciatica
Sciatica is the hallmark symptom of lumbar disc herniation. It manifests as a sharp, burning, or electric-shock pain that radiates from the lower back through the buttock and down the leg, following the path of the compressed nerve root. The exact distribution depends on the disc level involved:
- L4-L5 herniation: Pain radiates down the outer thigh and leg to the top of the foot and between the first and second toes.
- L5-S1 herniation: Pain travels down the back of the thigh and calf to the heel and outer edge of the foot.
Numbness and Tingling
Nerve compression from disc herniation frequently causes paresthesia. A “pins and needles” or numb sensation in the leg, foot, or toes corresponding to the affected nerve root. These sensations may be constant or intermittent and often worsen at night or after prolonged sitting.

Muscle Weakness
Motor nerve involvement may produce weaknesses in specific muscle groups. L4-L5 disc herniation commonly weakens when lifting the foot; potentially causing foot drops. L5-S1 herniation may impair calf strength, making it difficult to stand on your tiptoes. Prolonged weakness can lead to permanent muscle atrophy if untreated.
Cauda Equina Syndrome
Seek emergency medical care immediately if you experience loss of bladder or bowel control, saddle anesthesia (numbness in the groin and inner thighs), or sudden severe bilateral leg weakness. These are signs of cauda equina syndrome. A rare but serious complication requiring urgent surgical decompression to prevent permanent paralysis.
How Is a Herniated Disc Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis requires a thorough clinical evaluation combined with advanced imaging. At Deuk Spine Institute, diagnosis begins with the comprehensive Deuk Spine Exam, which identifies all potential pain generators with 99% accuracy.
Physical Examination
A neurological exam assesses muscle strength, sensation, and reflexes in the lower extremities. The straight leg raise (SLR) test also called the Lasègue sign. Is a sensitive test for lumbar disc herniation: pain radiating below the knee during passive leg elevation strongly suggests nerve root compression.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI is the gold-standard imaging tool for diagnosing lumbar disc herniation. It provides detailed visualization of the disc, annular tears, nerve root compression, and the degree of herniation. Crucially, MRI findings must always be correlated with clinical symptoms. For example, disc abnormalities are present in up to 60% of asymptomatic individuals over age 50. 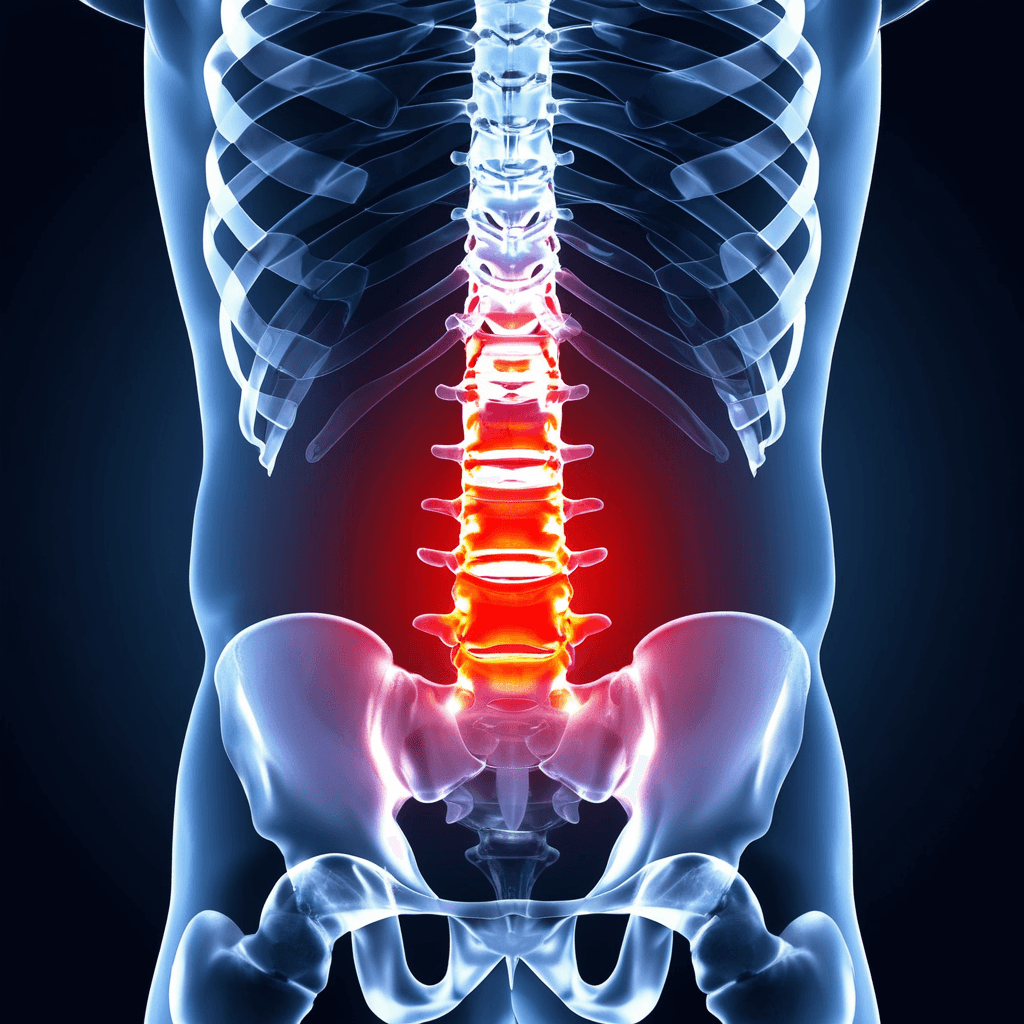
CT Scan / CT Myelogram
For patients who cannot undergo MRI, a CT scan or CT myelogram can provide detailed imaging of bony structures and neural elements.
Treatment Options for Herniated Disc in the Lower Back
Treatment decisions should be individualized based on symptom severity, duration, neurological status, and the patient’s goals. Most patients improve with conservative care; surgery is reserved for those with refractory symptoms or neurological compromise.
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatment
A systematic review published in 2024 confirmed that conservative treatment is effective at providing initial relief for most patients with lumbar disc herniation, with surgical intervention reserved for neurological deficits or treatment failure.3 A 2024 narrative review in the Journal of Clinical Medicine identified the following non-surgical approaches as having moderate evidence (Level B) of effectiveness:4
- Rest and activity modification: 1–2 days of rest during acute flares, followed by gradual resumption of activity. Prolonged bed rest is counterproductive.
- NSAIDs: The 2024 World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies (WFNS) guidelines confirm that NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) significantly reduce acute back and leg pain from disc herniation.
- Exercise therapy: A 2025 meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Medicine found that exercise therapy significantly improved pain scores, disability index, range of motion, and quality of life in lumbar disc herniation patients compared to controls, confirming it as an “economical, effective” first-line treatment.5
- Physical therapy: A comprehensive 2025 systematic review in Brain and Spine of 55 randomized controlled trials (4,311 patients) demonstrated that physical therapy effectively alleviates pain and improves function and quality of life following lumbar disc herniation.6 The McKenzie Method, core stabilization, and neural mobilization techniques are commonly recommended.
- Epidural steroid injections (ESIs): Corticosteroid injections into the epidural space can temporarily reduce inflammation and nerve irritation, providing a window for rehabilitative exercise. They are most effective for short-term relief.
- Oral corticosteroids and muscle relaxants: Short-course steroids may reduce acute inflammation; muscle relaxants help manage associated spasms.

Emerging Regenerative Therapies
A 2025 review in the Journal of Clinical Medicine evaluated emerging non-surgical treatments including platelet-rich plasma (PRP), bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC), and low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS).7 These Ortho biological approaches promote tissue regeneration and may reduce pain by stimulating disc healing, though they are not yet considered standard of care and require further clinical validation.
When Is Surgery Needed?
Only a small percentage of patients with lumbar disc herniation require surgery. According to current guidelines, surgery is indicated when:
- Conservative treatment has failed after an appropriate trial (typically 6–12 weeks).
- Progressive or severe neurological deficit is present (e.g., foot drop, significant weakness).
- Cauda equina syndrome is suspected (emergency surgery required).
- Pain is intractable and severely impacts quality of life.
Research indicates that surgical outcomes are more favorable when performed before 9 months of unresolved symptoms. A 2024 systematic review confirmed that earlier surgical intervention in patients with motor deficits is associated with faster recovery and better functional outcomes.
Deuk Laser Disc Repair®: A Minimally Invasive Solution
For patients who have exhausted conservative care or who require surgical intervention, Dr. Ara Deukmedjian pioneered the Deuk Laser Disc Repair®. A fully endoscopic outpatient procedure that directly eliminates the source of disc pain without spinal fusion, bone removal, or implants.
How DLDR® Works:
- A small 7mm incision is made in the lower back.
- An endoscope and a Holmium-YAG laser are guided to the herniated disc.
- The laser precisely vaporizes the herniated nucleus pulposus fragments inside the annular tear.
- Healthy disc tissue and surrounding structures are fully preserved.
- Patients walk within an hour of the procedure and are typically discharged on the same day.
Key Advantages:
- 99% success rate in eliminating pain with zero reported complications in over 2,000 procedures.
- No spinal fusion, rods, screws, or bone removal.
- No opioid painkillers required post-procedure.
- Preserves natural spinal motion and biomechanics.
- Published in peer-reviewed medical literature confirming safety and effectiveness.
Preventing Herniated Disc Recurrence
When you are managing a disc herniation conservatively the following evidence-based strategies help protect your lumbar spine and reduce recurrence risk:
- Core strengthening: Exercises targeting the transversus abdominis, multifidus, and gluteal muscles reduce lumbar disc stress.
- Proper lifting mechanics: Always bend at the hips and knees, not the waist, when lifting. Avoid rounding the lower back under load.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Reducing BMI decreases axial load on the lumbar discs.
- Avoid smoking: Nicotine reduces disc blood flow and accelerates degeneration.
- Ergonomic positioning: Use lumbar support when sitting; take standing breaks every 30–60 minutes.
- Low-impact exercise: Walking, swimming, and stationary cycling maintain cardiovascular health and disc nutrition without excessive spinal loading.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can a herniated disc heal on its own?
A: Some patients have spontaneous improvement as herniated disc material dehydrates and retracts. A 2025 case study published in the Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research documented complete spontaneous resorption of a severe L5-S1 herniation through conservative management over two years. However, because herniated discs have very limited blood supply, complete annular tear healing rarely occurs without targeted intervention. Symptoms may be resolved while the underlying structural damage remains.
Q: How long does it take to recover from a herniated disc?
A: Most patients with mild to moderate disc herniation improve within 4–12 weeks of conservative care. However, patients who continue non-surgical treatment beyond 9–12 months without improvement typically show poorer surgical outcomes. Making timely evaluation and escalation of care important.
Q: Is surgery always necessary?
A: No. Fewer than 10% of lumbar disc herniation patients require surgical intervention. Surgery is recommended when conservative care fails; neurological deficits progress, or cauda equina syndrome is present.
Q: Can a herniated disc cause leg pain without back pain?
A: Yes. In some cases, a herniated disc causes radicular leg pain (sciatica) with minimal or no localized back pain. The disc material may compress a nerve root without significantly affecting local spinal structures. This pattern is common with L4-L5 and L5-S1 herniations.
Sources
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
2. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9560562/
3. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11425427/
4. https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/13/4/974
5. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1531637/full
6. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772529425000578